Is invoice factoring a loan? No, it’s not. Invoice factoring means selling your unpaid invoices to get immediate cash and is considered a sale, not a loan. This article explains how invoice factoring works, its pros and cons, and how it compares to traditional loans.
Takeaways
- Invoice factoring is a sale of receivables providing immediate cash flow, not a loan, unlike traditional borrowing methods.
- Key differences between invoice factoring and traditional loans are credit requirements, repayment structure and speed of access to funds.
- Businesses must evaluate factoring companies on reputation, fee structures and service quality to get the most out of invoice factoring.
What is Invoice Factoring
Invoice factoring is essentially a sale of receivables not a loan. It means selling unpaid invoices to a factoring company for immediate funds, providing businesses with instant cash flow by converting their receivables into cash quickly. This helps businesses manage cash flow issues and cover short term expenses, making it an essential tool for operations and growth.
Definition of Invoice Factoring
Invoice factoring is selling unpaid invoices to an invoice factoring company at a discount. Factoring companies buy these invoices and provide immediate cash flow to businesses.
Unlike traditional loans, invoice factoring is legally classified as a sale of invoices, not a debt instrument, which is different from conventional borrowing methods.
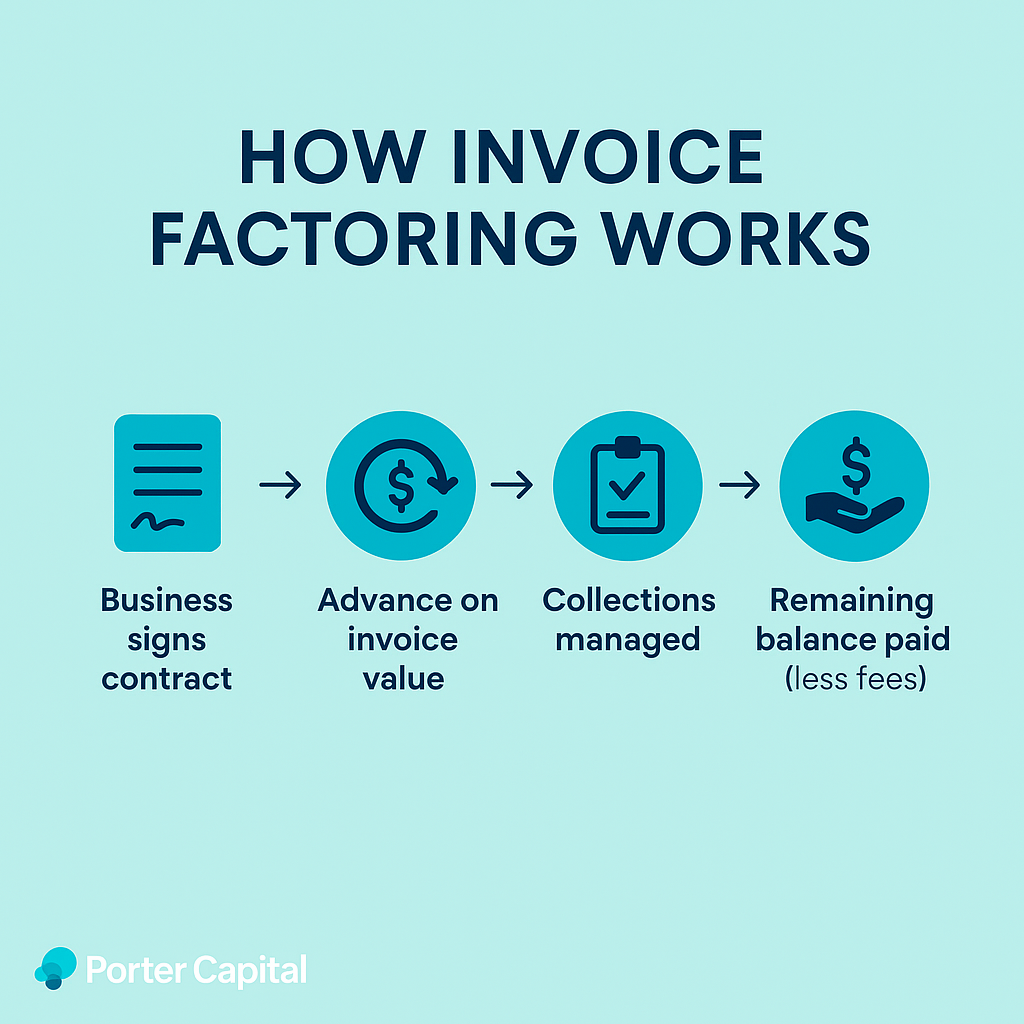
How Invoice Factoring Works
Invoice factoring starts with the business signing a contract with a factoring company. The business then gets an advance on the invoice amount, usually 70% to 90% of its value. The factoring company takes over collections from customers, managing payments efficiently.
Once the customer pays, the factoring company pays the remaining balance to the business, minus their fees. This simplifies the business’s work and boosts working capital.
Invoice Factoring vs Traditional Loans
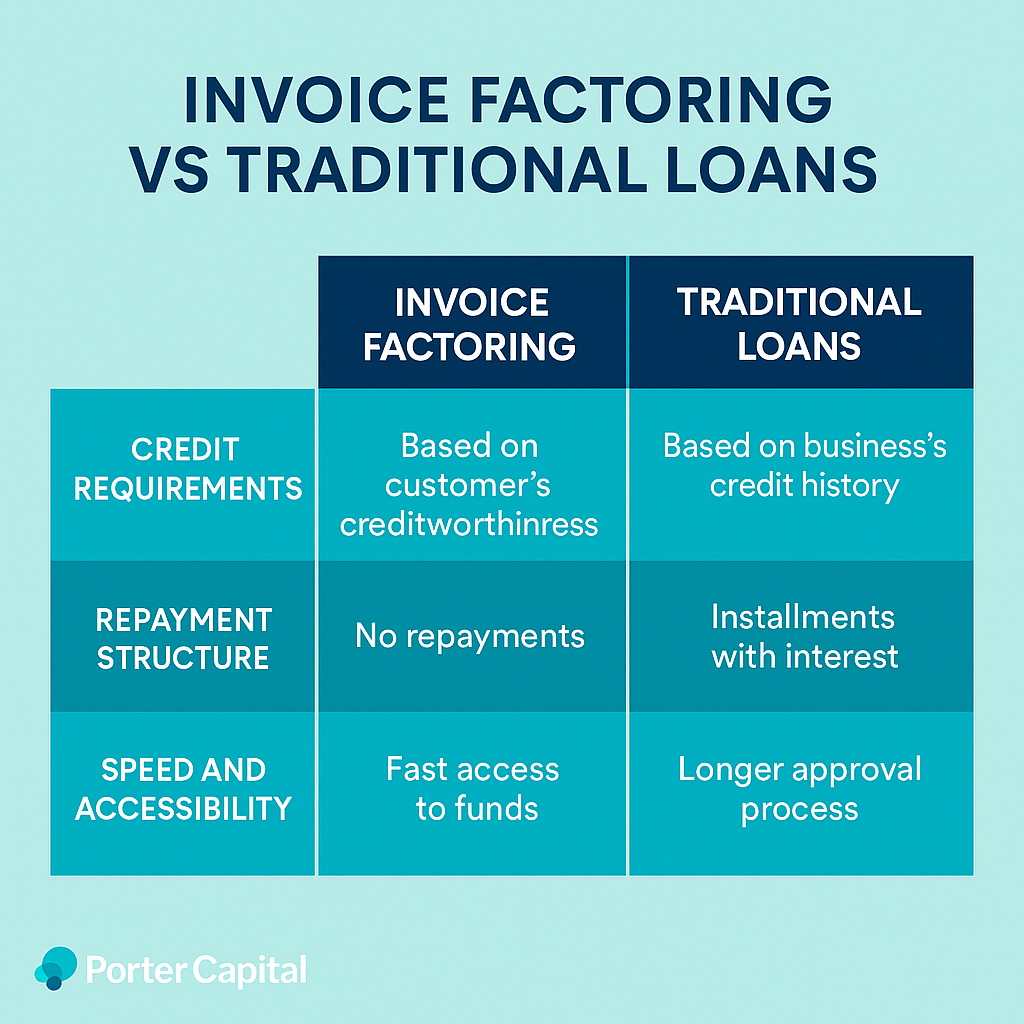
Invoice factoring and traditional loans have many differences. Invoice factoring means selling unpaid invoices for immediate cash, while traditional loans are borrowed funds repaid over time with interest.
Knowing these differences will help businesses make better financial decisions.
Credit Requirements
One of the main differences between invoice factoring and traditional loans is the credit requirements. Invoice factoring focuses more on the customer’s creditworthiness to pay rather than the business’s credit history. Factoring companies have less stringent approval requirements than traditional loans which require substantial assets or a good credit history to qualify. A financing company can be an alternative for those who need quick funding.
Repayment Structure
Unlike traditional loans that require regular repayments, invoice factoring provides cash upfront with no repayment structure. This gives more cash flow flexibility.
This is more beneficial for businesses that need immediate capital without the burden of a repayment schedule.
Speed and Accessibility
One of the advantages of invoice factoring is the speed of access to funds. Many factoring companies can provide cash within 24 hours of submitting invoices. The approval process for invoice factoring is much faster than traditional loans, often taking just a few days compared to the longer approval periods for bank loans.
Is Invoice Factoring Debt?
Invoice factoring is not debt. It’s the sale of accounts receivable not borrowing money.
This is important for businesses that want to control their finances without increasing liabilities.
Legal Classification
Legally, invoice factoring is a sale of receivables. There is no repayment involved as businesses sell their unpaid invoices to a factoring company for immediate cash. This is different from traditional debt instruments making it a unique receivable financing option.
Impact on Business Finances
Invoice factoring affects business finances by transferring receivables ownership to the factoring company. This provides immediate working capital through selling accounts receivable financing and accounts receivable factoring without increasing balance sheet debt.
In recourse factoring, businesses must repay the factor for any unpaid invoices which can affect financial planning.
Types of Invoice Factoring

Understanding the different types of invoice factoring is crucial to choose the right one for your business. Common types are recourse factoring, non-recourse factoring and spot factoring.
Recourse Factoring
In recourse factoring, the business is liable for unpaid invoices. This option usually has lower fees than non-recourse factoring but the business must cover any losses from uncollected invoices.
Non-Recourse Factoring
In non-recourse factoring, the factoring company assumes the risk of non-payment by customers. This option is more expensive as the factoring company takes on more risk but provides businesses protection against client non-payment.
Spot Factoring
Spot factoring is factoring one invoice at a time. This allows businesses to get funds for a large outstanding invoice immediately but may come with higher costs or more stringent qualifying criteria especially for factored invoices.
Costs of Invoice Factoring
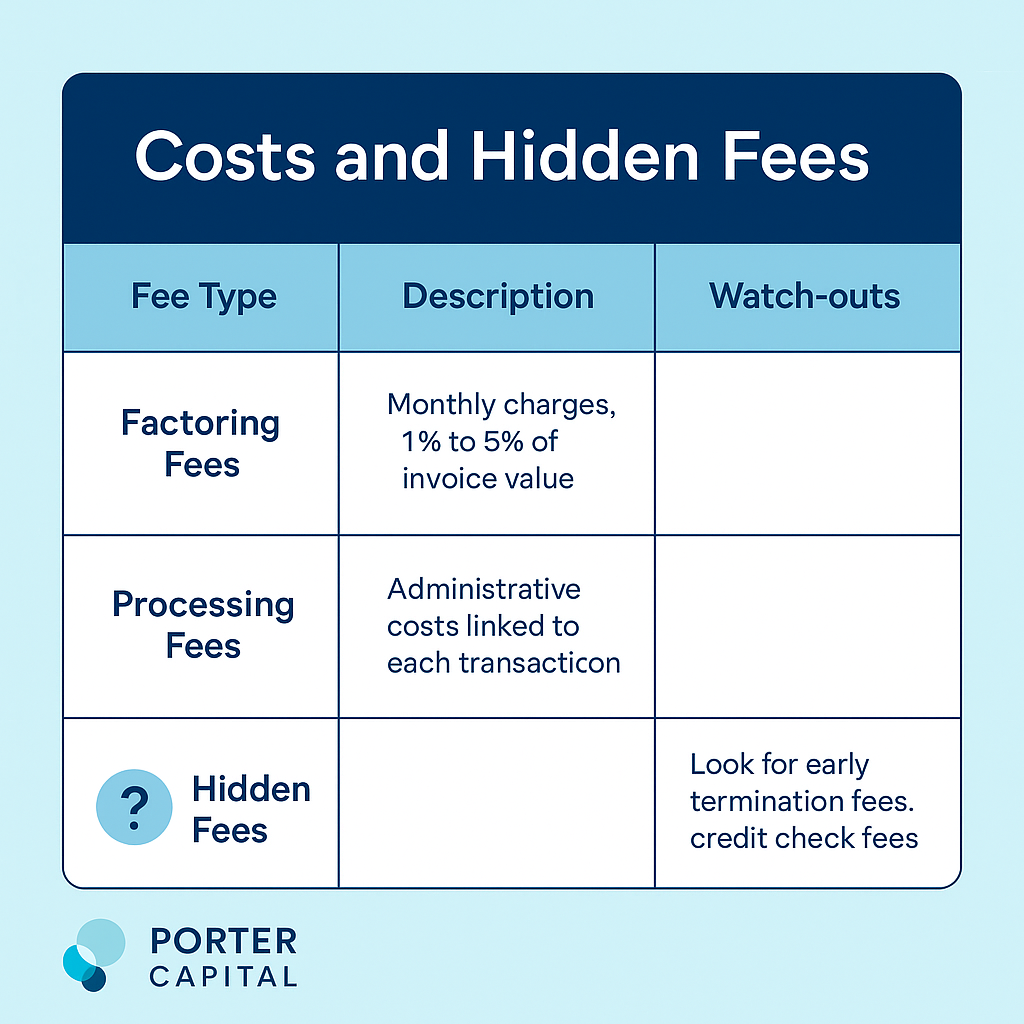
Invoice factoring has various costs businesses need to consider, including invoice factoring cost. Typical factoring fees range from 1% to 5% of the invoice value per month depending on the invoice amount and the client’s creditworthiness.
Factoring Fees
Common fees in invoice factoring are service fees, processing fees and factoring fee charge fees. These fees can impact the overall cost of factoring so businesses should understand the fee structure and ask about any additional charges.
Hidden Fees
Factoring agreements may have hidden fees like credit check fees, late payment penalties, additional fees for early termination and higher fees for early termination. Review the factoring agreement carefully to avoid unexpected costs and ensure overall cost-effectiveness.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Invoice Factoring
Invoice factoring has advantages like improved cash flow and easier qualification for businesses with poor credit. However, it also has drawbacks like higher costs and potential risk to customer relationships.
Benefits
One of the primary benefits of invoice factoring is the immediate cash flow without increasing balance sheet liabilities. This is more beneficial for startups or businesses with poor credit, providing access to working capital without a strong credit history.
Drawbacks
On the other hand, invoice factoring can be more expensive than traditional financing options. Fees can vary greatly depending on how quickly customers pay their invoices and aggressive collection tactics can damage client relationships and reputation.
Choosing the Right Factoring Company

Choosing the right factoring company maximizes the benefits of invoice factoring. Evaluating the reputation, fee structures and industry experience of different factoring companies helps align their services to your business needs.
Evaluating Factoring Companies
Consider the reputation, advance rates and customer support quality when evaluating factoring companies.
Check if they specialize in your industry as this can affect service quality and cost.
Questions to Ask
Questions to ask potential factoring partners are their policies on recourse and non-recourse factoring, the flexibility of their funding solutions and transparency in their terms and conditions to avoid hidden charges.
Alternatives to Invoice Factoring
While invoice factoring is an option, businesses can also consider other financing methods like traditional bank loans, lines of credit, alternative financing, invoice financing and factoring and crowdfunding.
Traditional Bank Loans
Traditional bank loans are generally more cost-effective but time consuming to get. They may not be suitable for businesses with poor credit or limited assets especially when considering a bank loan.
Lines of Credit
Business line of credit offers flexible access to funds, businesses can withdraw amounts as needed and pay interest only on the drawn funds. This flexibility can be a big advantage over other financing methods like invoice factoring.
Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding lets businesses raise capital from many people via online platforms. This is more suitable for startups and small businesses with projects that appeal to a community or specific demographic.
Conclusion
In conclusion, invoice factoring is a unique financing option that provides immediate cash flow by converting receivables into cash. Unlike traditional loans, it doesn’t increase debt on the balance sheet and provides faster access to funds. However, it comes with higher costs and potential risk to customer relationships. By understanding the differences, costs and types of invoice factoring, businesses can make informed financial decisions that suits their needs.
FAQs
Is invoice factoring a loan?
Invoice factoring is not a loan; it’s selling unpaid invoices to a factoring company for quick cash.
What are the costs of invoice factoring?
Invoice factoring has costs like factoring fees of 1% to 5% of the invoice value plus potential hidden charges like credit check fees and late payment penalties. Be aware of all costs when considering this financing option.
How does invoice factoring affect business finances?
Invoice factoring positively affects business finances by providing immediate working capital without increasing debt. However, businesses must be careful with recourse factoring as they may need to repay for unpaid invoices.
What are the types of invoice factoring?
The main types of invoice factoring are recourse factoring where the business is liable for unpaid invoices; non-recourse factoring where the factor assumes the risk and spot factoring which allows factoring of a single invoice. Understanding these options can help you choose the right solution for your financial needs.
What are alternatives to invoice factoring?
Try traditional bank loans, lines of credit or crowdfunding instead.



